Platform Introduction
Based on the functional testing platform of MiniPDX, Shanghai Lewen has published many academic papers, mainly SCI, through in-depth research collaboration with clinical experts.
On the one hand, our clinical testing service based on MiniPDX can assist clinicians in the translation of clinical research results by using MiniPDX to guide clinical drug use; on the other hand, we have a comprehensive research service platform based on functional testing, multi-omics testing, and proteomics, including PDX and MiniPDX. On the other hand, we can assist the translation of basic research by relying on our comprehensive research service platform of functional assays, multi-omics assays, and proteomics including PDX and MiniPDX.
In the field of clinical research, controlled studies and single-arm studies of MiniPDX-based precision therapy protocols covering various tumor types have been published, which deepen the evidence of MiniPDX; in addition, we are looking forward to further cooperation with experts in other fields/tumor types of precision therapy.
In the field of basic research, the "gold standard" pharmacokinetic study represented by PDX has been widely used in the field of oncology research and has become a necessary tool for the translation of high-level results. The application potential is also favored by more and more experts.
Summary of Academic Results
1. Characterization of drug responses of mini patient‑derived xenografts in mice for predicting cancer patient clinical therapeutic response
2. Guided chemotherapy based on patient‑derived mini‑xenograft models improves survival of gallbladder carcinoma patients
3. Personalized treatment based on mini patient‑derived xenografts and WES/RNA sequencing in a patient with metastatic duodenal adenocarcinoma
4. Integrated Omics of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
5. A Novel, Personalized Drug-Screening System for Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer Patients: A Preliminary Clinical Report
6. MiniPDX‑guided postoperative anticancer treatment can effectively prolong the survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
7. Mini-Patient-derived Xenograft Model Based on Microfluidic Technology Promises to be an Effective Tool for Screening Individualized Chemotherapy Regimens for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
8. XPO1 inhibition synergizes with PARP1 inhibition in small cell lung cancer by targeting nuclear transport of FOXO3a
9. Circulating Cell-Free DNA-Based Detection of Tumor Suppressor Gene Copy Number Loss and Its Clinical Implication in Metastatic Prostate Cancer
10. Xenograft tumors derived from malignant pleural effusion of the patients with non‑small‑cell lung cancer as models to explore drug resistance
11. 人源化免疫肺癌小鼠模型的建立及其在程序性死亡受体1抑制剂疗效评估中的作用
12. OncoVee MiniPDX (TM)模型指导驱动基因阴性的晚期非小细胞肺癌患者化疗的疗效分析
13. MiniPDX模型在晚期肺癌伴恶性胸腔积液患者治疗中的指导作用
14. 间接体内Mini人源肿瘤异种移植模型再现转移性肠癌患者的药物治疗疗效
15. 用于预测癌症患者临床治疗方案的小鼠mini人源肿瘤异种移植模型的建立
Application Examples
MiniPDX-guided post-operative drug regimen significantly prolongs survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Recently, Prof. Yamin Zhang's team at Tianjin First Central Hospital published a new research paper in the prestigious journal Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology entitled "MiniPDX-guided postoperative anticancer treatment can effectively prolong the survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma". The article shows that using the MiniPDX model drug sensitivity assay to guide postoperative anticancer treatment after partial hepatectomy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma significantly prolongs patient survival. Median overall patient survival was extended from 23.8 months to 29.4 months; median disease-free survival was extended from 18.2 months to 25.8 months.

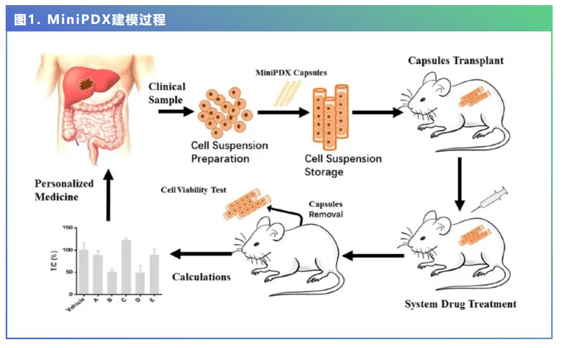
The study enrolled 28 HCC patients and used their tumor tissues to establish a mini patient derivedxenograft (MiniPDX model) and tested the proliferation rate of tumor cells under 5 different prophylactic regimens (5-FU+oxaplatin, gemcitabine, levatinib, regorafenib, sorafenib) after partial hepatectomy. sorafenib) to screen for the most sensitive drug regimen for patients.
The investigators also selected 42 HCC patients treated with the empirical regimen sorafenib as the control group; analyzed the disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) in both groups; and analyzed the correlation between drug sensitivity and HCC-related biomarkers (including AFP, Ki-67, VEGFR, FGFR, P53, and Nrf2).
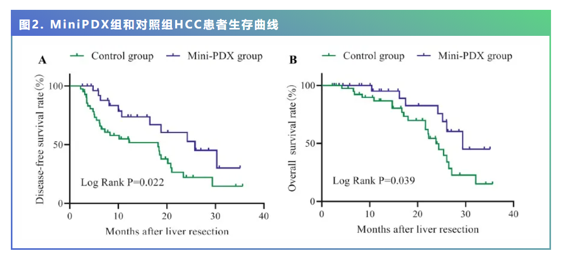
The results showed that at a maximum follow-up of 36 months, the median OS of HCC patients treated with the MiniPDX screening regimen was 29.4 months, significantly longer than that of patients treated with the conventional regimen at 23.8 months (p=0.039). The median DFS for patients on the MiniPDX regimen was 25.8 months, again significantly longer than the 18.2 months for patients on the conventional regimen (p=0.022).
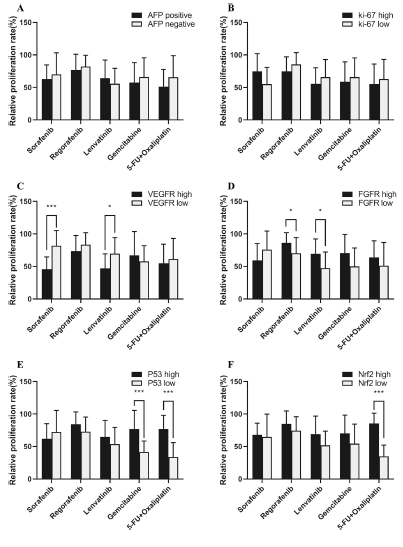
In addition, the researchers found that different drug sensitivities showed some correlation with HCC biomarkers: sorafenib and levatinib showed higher antitumor activity in patients with high VEGFR expression; HCC patients with high FGFR expression were more sensitive to regorafenib and levatinib; while patients with high P53 mutations showed some degree of tolerance to cytotoxic drugs; and 5-FU combined with oxaliplatin showed stronger cytotoxicity in HCC patients with low Nfr2 expression.




-227.jpg)
