Products
Glioma genetic testing
① Glioma is the most common primary intracranial tumor, accounting for approximately 27% of all CNS tumors and approximately 80% of malignant tumors
② Several CNS clinical guidelines have incorporated molecular detection of glioma, and the 2016 WHO CNS tumor classification guidelines have introduced the first classification method integrating histological phenotype and genetic phenotype.
③ For a long time, CNS tumor classification has been mainly based on histological features: studies in recent decades have found that tumors with the same histological features have different molecular genetic differences; it is these molecular genetic differences that make patients with the same grade of tumor have different prognosis and drug sensitivity.
④ Genetic testing is a necessary complement to conventional pathology. Genomics-based molecular typing can provide accurate and objective genetic information for tumor diagnosis, prognosis and treatment, and help clinicians understand the specific tumor characteristics of each individual patient from a new perspective of molecular biology, so as to specify treatment plans in a more targeted manner.
Glioma test 6/8 items package
Product Advantages
01、Precise molecular typing guidance
The product design refers to the guideline recommendation, and the detection items of IDH1 mutation, IDH2 mutation, 1p19q joint deletion and TERT mutation are powerful supplements to the traditional pathology.
02、Drug sensitivity and targeted dosing guidance
The results of MGMT promoter methylation can be used to predict the efficacy of alkylating agent chemotherapy, and BRAF, as an important gene in MARK signaling pathway, is associated with several targeted drugs, which may provide patients with more choices of targeted drugs for treatment.
03. High-precision detection method
No control sample is required, and for point mutations, a one-step method (multiplex PCR combined with NGS sequencing) is used to maximize the comprehensiveness and accuracy of the results.
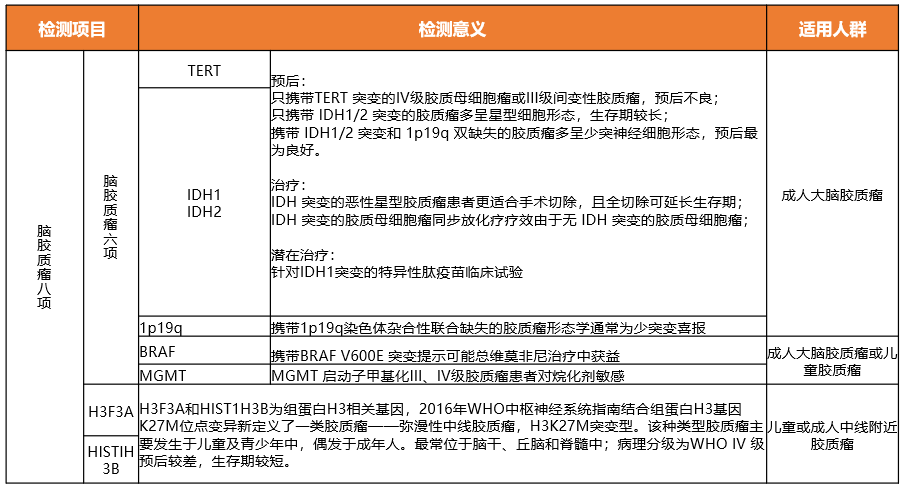
Clinical Significance
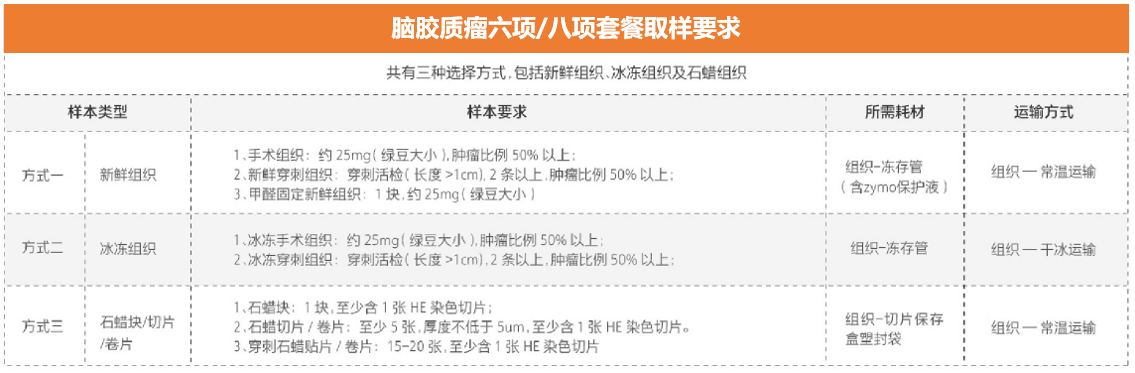
Sampling requirements